vu
Notes for Vanderbilt University
Final Exam
Unit 1
- information sec CIA triangle
- confidentiality
- more confidentiality, more control
- more confidentiality, less access
- integrity
- data degradation types:
- invalid
- redundant
- inconsistent
- anomalous
- read inconsistency
- nonconcurrency
- data degradation types:
- availability
- confidentiality
- risk: threat, vulnerability, impact
- lifecycle:
- design
- implement
- check
- maintain
- default security: full mediation
- design principles
- simplicity > complexity
- default = block
- all access must be filtered
- transparent sec against dark sec
- segregation of duties
- minimum priviledge
- minimum common mechanisms
- user acceptability
- working factor
- event log
Unit 2: Malware
- types
- worm
- autonomous
- replicates & spreads
- virus
- programs contained in others
- phases:
- propagation
- latency
- activation
- damage
- types:
- metamorphic: change every iteration
- polymorphic: change only parts to prevent detection
- trojan horse
- logic bomb
- unexpected effect
- backdoor
- undocumented / secret
- worm
- taxonomy
- only worms are autonomous
- only worms and viruses are self reproducing
- APT: advanced persistent threat
- malware designed to stay undetected
- detection:
- large # of reqs from same IP
- transmission of large amounts of data
- 3rd party warnings
- ex:
- stuxnet
Unit 3: Access Control Systems
- representation
- ACL / matrix
- regular: object -> users
- habilitation: user -> objects
- auth relations: tuples of (S, O, rights)
- ACL / matrix
- DAC
- same but with owners
- multilevel security:
- BLP (bell lapadula)
- data confidentiality
- rules
- read all under
- if can read 1 and write 2, l(1) <= l(2) (* property)
- cannot write on lower
- no change in levels
- BIBA
- data integrity
- rules
- cannot read from a lower level
- if can read 1 and write 2, l(1) >= l(2) (* property)
- cnanot write on higher
- no change
- Clark Wilson
- integrity
- problems:
- expensive
- complex administration & conversion of current system
- prevents unauth’d but also auth’d
- BLP (bell lapadula)
- multilateral:
- chinese wall
- grants if:
- p in set of company already with access
- p does not belong to conflict of interest
- s can write o if never read o’ (CoI) (* property)
- grants if:
- chinese wall
- multilevel & multilateral
- classification level
- o: (compartment, confidentiality)
- s: (compartment, habilitation)
- o_i <= s_i
- classification level
Unit 4: Distributed Systems Protocol
- threats
- passive
- interception
- war driving
- port scan
- active
- interruption
- ddos
- icmp flood
- tcp-syn
- modification
- ip spoof
- pharming
- dns identity theft
- generation
- session hijacking
- interruption
- passive
Unit 4: SSL/TLS
- SSL protocols
- handshake
- change cipher spec
- alert / warning
- record
- security services
- confidentiality
- crypto
- integrity
- mac
- auth
- one way funcs
- question answer
- e-sign
- access control
- non-repudiation
- confidentiality
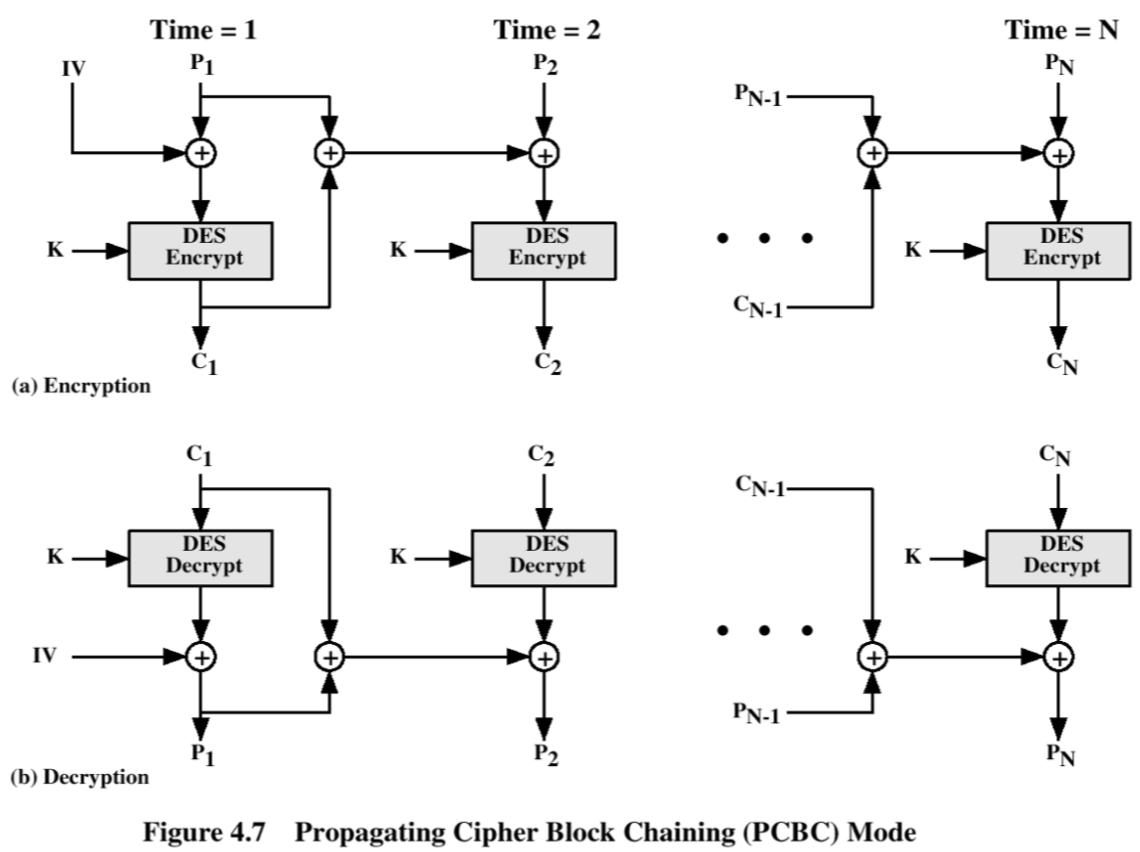
Unit 4: Kerberos
- centralized auth server
- symmetric encryption (DES)
- uses propogating cipher block chain
Unit 4: IPSec
- security issues in IP
- networks are not secure since all users were originally known
- IPSec: standard for network layer security
- auth protocol (AH auth header)
- encryp / auth protocol (ESP encapsulated security protocol)
- mandatory for IPv6